Research FindingsBack
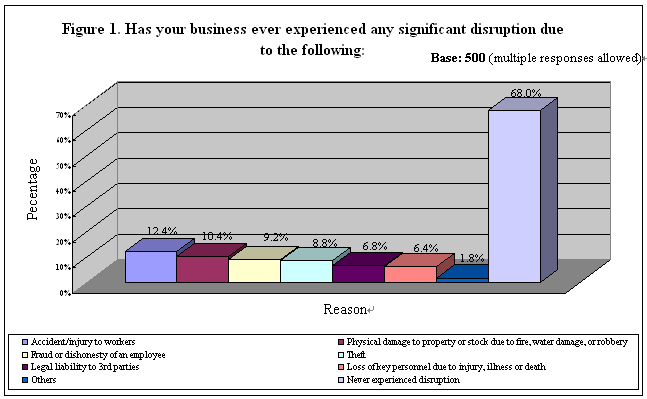
This survey comprised 9 simple opinion questions and ended by mapping some basic demographics of the company/respondent. The key findings of these questions are summarized below. Cross-references could be made with the tables in Appendix 2. Business Disruption in the Past The survey began by asking the respondents whether their business had experienced any serious disruption due to a number of factors. Results revealed that the majority (68%) of the SMEs interviewed had never experienced significant disruption before, while a respective of 12% and 10% said their business was seriously disturbed by 「accident/injury to workers」 and 「physical damage to property or stock due to fire, water damage or robbery」. About one-tenth were affected by 「theft」 (9%) and 「fraud or dishonesty of employees」 (9%). Relatively fewer companies had encountered disruption due to 「legal liability to 3rd parties」 (7%), 「loss of key personnel due to injury, illness or death」 (6%) and also some other problems (2%, Table 3). See Figure 1.
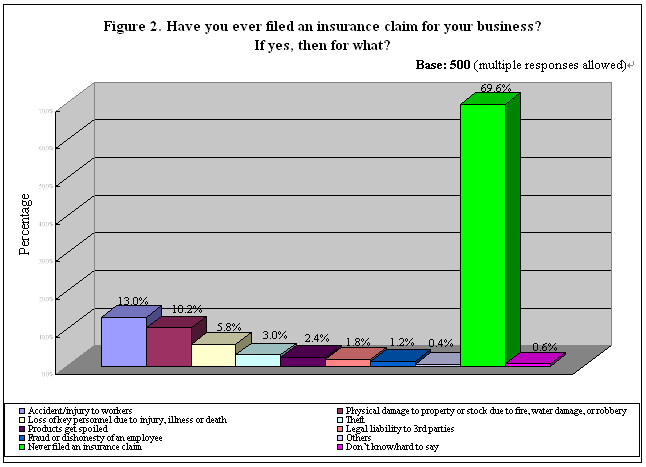
Consistent with the finding that many SMEs had not experienced any serious disruption to their business prior to the interview, as high as 70% had not filed an insurance claim either. Meanwhile, 13% of the overall sample made a claim for 「accident/injury to workers」. 「Physical damage to property or stock due to fire, water damage or robbery」 and 「loss of key personnel due to injury, illness or death」 claims followed behind, which accounted for 10% and 6% respectively (Table 4). See Figure 2 for all categories.
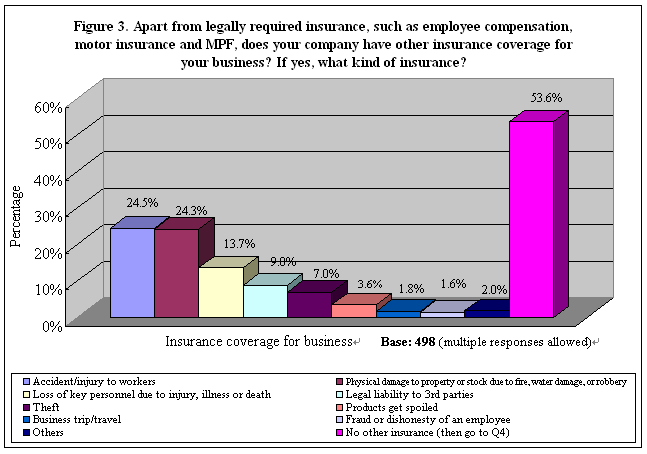
Existing Insurance Coverage Apart from legally required insurance, such as employee compensation, motor insurance and MPF, around one-quarter of the respondents' companies were insured against 「accident/injury to workers」 (25%) and 「physical damage to property or stock due to fire, water damage or robbery」 (24%). Another 14% had insurance coverage for the 「loss of key personnel due to injury, illness or death」. However, more than half (54%) of the respondents said their business was not protected by other kinds of insurance (Table 5). See Figure 3.
When further asked why they did not go for other kinds of insurance apart from those legally required, 58% of this sub-group said 「it was not important」 to their business. Another 18% did not have it because they thought 「it was too expensive」 while 14% believed 「it was not necessary」 as fulfilling the legal requirement was already good enough. Besides, over one-tenth (12%) admitted they were ignorant about what insurance product was available in the market and finally, 7% said 「it was too complicated」 (Table 6). See Figure 4.
The survey continued to ask the respondents what insurance benefits they had offered to their employees. Results revealed that 52% of the SMEs interviewed offered nothing to their employees in this aspect, whereas 43% had 「medical insurance」 and 13% provided 「life insurance」 as well. The percentage of 「other personal insurance」 accounted for 11% of the total sample (Table 7). See Figure 5.
For those who had offered 「life, medical and/or personal insurance」 to their employees, 62% agreed that such benefits could help attract and retain staff (18% opted for 「very much agreed」 and 43% 「somewhat agreed」), representing the majority opinion. On the contrary, 15% disagreed (12% said 「somewhat disagreed」 and 3% 「very much disagree」). Another 22% chose 「half-half」 and the remaining 2% failed to make a judgment on this (Table 8). See Figure 6.
For those who did not provide any insurance benefits to their staff, the survey further probed their reasons behind. It is found out that the 「cost consideration」 was the most common hindrance as cited by these employers (28%), closely followed by the option that 「employees were more interested in cash salary」 (24%). Other popular reasons included 「the existing benefits were sufficient / it was not necessary」 (19%), 「no staff / small number of staff」 (11%), 「unsure what to offer」 (10%) as well as 「administrative problem」 (10%, Table 9). See Figure 7 for more answers.
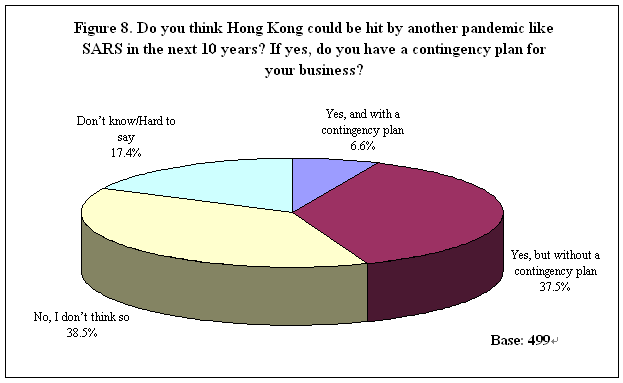
Future Plan for Pandemic like SARS As the last part of the survey, all respondents were asked if they thought Hong Kong would be hit by another pandemic like SARS in the next 10 years. Results showed that 44% of the SMEs in this sample said 「yes」 but only 7% had a contingency plan for this while the remaining 38% were not prepared. Another 39% thought it was not likely to have another pandemic striking Hong Kong within the next decade, and hence remained unprepared too. Finally, 17% could not even give a definite answer (Table 10). In other words, only less than 10% of these companies had contingency planning if another pandemic really occurred in near future. See Figure 8.
The survey ended by a follow-up question with those who answered 「yes, and with a contingency plan」 for yet another pandemic in the next 10 years (33 respondents only) to see if insurance was part of their plan. Results showed that 46% (15 respondents) said 「yes」 whereas 55% (18 respondents) did not have any insurance element in their future plan (Table 11). See Figure 9.
|